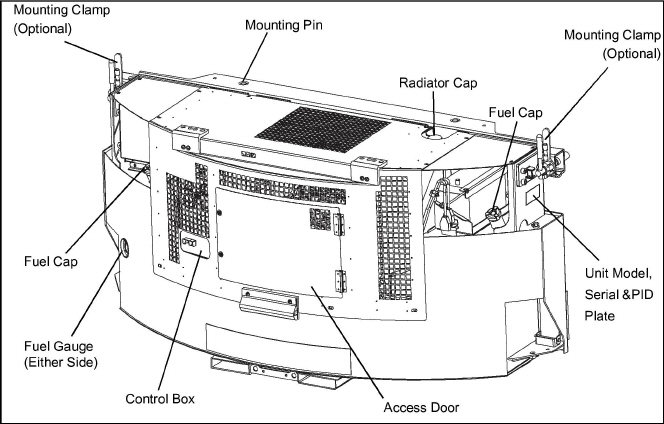
Section 2
The Carrier Transicold model 69RG15 clip-on diesel driven generator sets provide electrical power for all-electric refrigeration units.
The generator set (see Figure 2.1 and Figure 2.2) consists of a diesel engine directly connected to an alternating current generator and mounted in a structural steel frame. The engine is a vertical in-line, four cylinder diesel manufactured by Kubota. The generator is a 15 kW, permanent, dual bearing type. Generator sets will start at 50Hz. Once the unit is running, the voltage controller will read the voltage output of the generator and adjust accordingly to keep the voltage within ISO limits. As the Container becomes loaded, voltage drops and current increases, causing the generator set to switch windings or speed based on power demand and ambient conditions. The unit will typically run at 50Hz and will vary generator output via winding selection. The speed change to 60 Hz will typically occur when the ambient temperature is high and the unit is heavily loaded.
Electrical controls are mounted in a control box with operating controls and gauges mounted on a control panel (which also serves as the control box cover). The control panel components are protected by a deflector assembly.
Auxiliary engine equipment consists of the battery, solid state battery charging system, “spin-on” lube oil filter, fuel filter and other necessary components for proper unit operation. The water pump and the radiator cooling fan are belt-driven from the engine crankshaft. All references to engine are as viewed from the fly wheel end.
The 69RG15 is available as a standard configuration, with an Auto Restart option. The Auto Restart option automatically restarts the unit in the event of specific unit shutdowns.
Carrier Transicold’s Ecodriven dual speed option provides an energy saving alternative to the practice of continuously running the generator at full speed. This speed reduction results in increased fuel economy, reduced carbon footprint, and lowers operating costs.
2.2Configuration Identification
Generator set identification information is provided on a label located below the right mounting clamp (front facing). The label provides the generator set model number, serial number and parts identification number (PID). The model number identifies the overall configuration while the PID provides information on specific optional equipment and differences in detailed parts.
The model number, serial number and PID number must be included when ordering parts and inquiring about your unit.
Separately bound manuals covering the diesel engine are also available. (See Table 2–1).
Manual /Form Number |
Equipment Covered |
Type of Manual |
|---|---|---|
62-11335 |
V2203-DI |
Engine Part List |
62-11362 |
V2203-DI |
Workshop |
Figure 2.2 Generator Set - Top Cover Removed
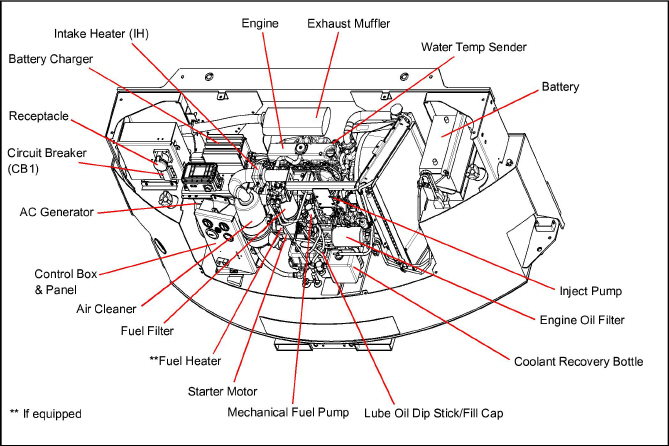
The engine is a vertical, in-line four cylinder diesel engine that is directly connected to the alternating current generator. Information on the major engine systems is provided in the remainder of this chapter.
2.3.1Electronic Governor Module
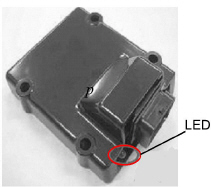
The electronic governor module (EG) is a solid state control module preprogrammed for 1800 RPM high speed and 1500 RPM low speed operation.
The unit has an LED which may be used to diagnose failures within the electronic speed control system, refer to Section 4.5 for additional troubleshooting information on diagnosing failures.
Figure 2.3 Electronic Governor Module
The air cleaner (Figure 2.2) is designed to prolong engine life and performance by preventing dirt and grit from entering the engine and causing excessive wear on all operating parts. In order for the air filter to operate properly, the operator must regularly maintain the air cleaner equipment in accordance with the instructions provided within this document.
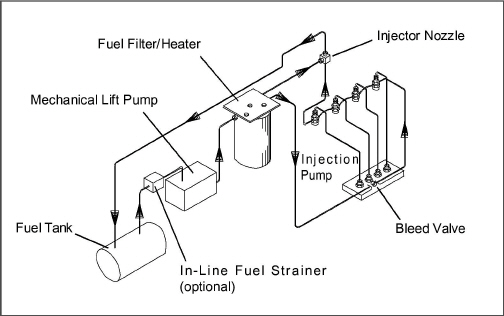
The fuel system is fitted with an optional in-line fuel strainer and a fuel filter, which also acts as a water separator. The fuel system is shown in Figure 2.4.
The fuel heater system is located in the fuel filter, and uses a 12 volt heater to heat fuel as it passes through the fuel filter.
Figure 2.4 Fuel System Diagram
2.3.4Lube Oil Filter Arrangement
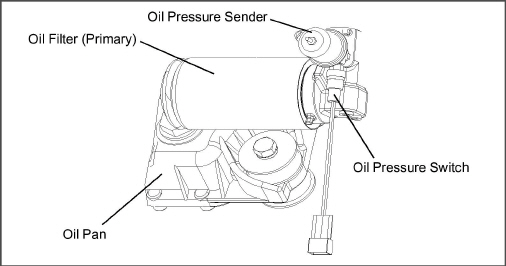
The engine lubricating oil filter is mounted in a horizontal arrangement and is shown in Figure 2.5.
All threads on the engine are metric, except for the oil drain plug which is American Standard Pipe Thread (NPT).
2.5Alternating Current Generator
The generator bolts directly to the engine and supplies nominal 50/60Hz power depending on the load requirement.
The solid state battery charger (see Figure 2.2) is located on top of the generator. The battery charger is powered by the generator, and this input is protected by fuses located in the receptacle box. The battery charger produces a tapered charge (40 amps maximum) and is designed not to overcharge the battery.
Observe proper polarity when installing the battery or connecting a battery charger. The negative battery terminal must be grounded. Reverse polarity may damage the charging system. When charging the battery in unit, isolate the battery by disconnecting the negative battery terminal first, then the positive. Once the battery has been charged, connect the positive battery terminal first, then the negative.
Voltage Controller maintains ISO voltage via two-speed and dual winding control. It regulates voltage in order to keep the generator output within ISO limits:
•50Hz: 1500 RPM, 360-460 VAC
•60Hz: 1800 RPM, 400-500 VAC
2.8Operating Controls & Instruments
Components required for monitoring and controlling the unit are located in the control box, on the control panel (seeFigure 2.1) and on the receptacle box (see Figure 2.1).
2.8.2Control Panel and Related Components
1.Gauges and Senders
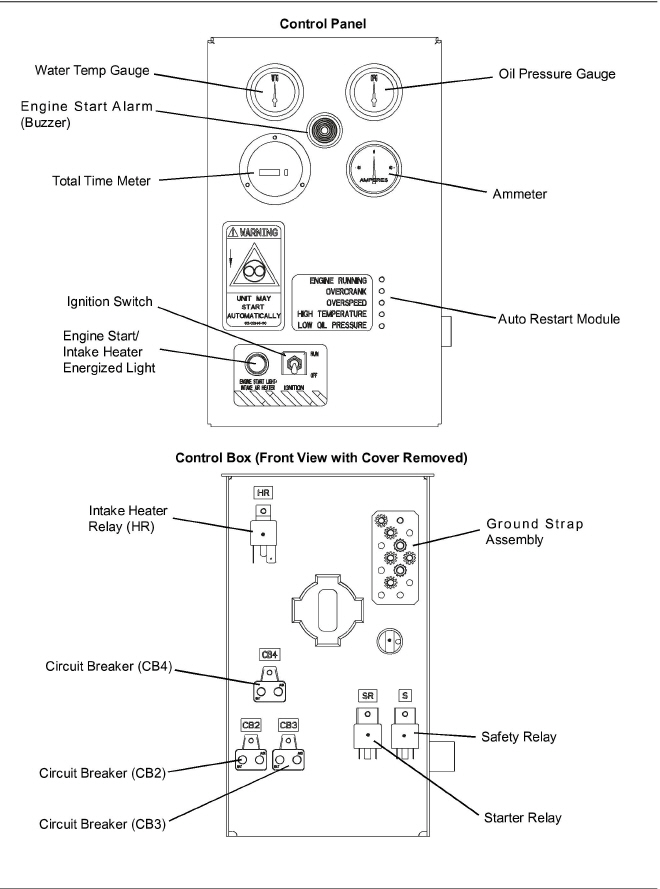
a.Oil Pressure Gauge (see Figure 2.6 or Figure 2.7)
The purpose of this gauge is to observe normal operating engine oil pressure. Normal oil pressure is 35 to 60 psig (3.3 to 5.2 kg/cm2).
b.Oil Pressure Sender (see Figure 2.5)
This device senses engine lube oil pressure and transmits a signal to the oil pressure gauge. The oil pressure sender is located on the oil filter housing.
c.Water Temperature Gauge (see Figure 2.6 or Figure 2.7)
The function of this gauge is to observe water operating temperature. The gauge is connected to the water temperature sender.
This device (see Figure 2.2) senses engine water temperature and transmits a signal to the water temperature gauge. The water temperature sender is located on the top, left-hand side of the engine below the high water temperature switch.
e.Auto Restart Module (If Equipped) (see Figure 2.7)
Auto start/restart is provided to simplify the start-up process and provide an automatic restart feature that will automatically attempt to restart the unit in the event of some shutdowns. Four LEDs are used to indicate shutdown from overcrank, overspeed, low oil pressure, and high water temperature. A fifth LED is used to indicate the unit is running. Refer to Table 2–2 for system preset values.
The auto restart function will perform a series of six attempts to restart the unit and make three attempts within each series. Once the function has completed all 18 attempts the unit will automatically lock out future crank attempts. Refer to Table 2–3 for detailed information on auto restart sequencing.
a.Ammeter (A) (see Figure 2.6 or Figure 2.7)
The ammeter is an indicator of the charging system and unit electrical draw. It indicates the rate of discharge or charge of the battery. During start up, the intake heater draws approximately 42 amps.
b.Total Time Meter (TT) (see Figure 2.6 or Figure 2.7)
This meter designates the total hours and provides an accurate readout of accumulated engine running time. This data can be used to establish the proper periodic maintenance schedule. (Refer to Table 5–1.)
The intake heater switch is of the momentary type. When held in the PREHEAT position, the switch allows approximately 42 amps of battery current to flow into the intake heater. This, in turn preheats the air within the intake manifold and allows the engine to start. After starting the engine, the intake heater switch should continue to be held in the ON position for approximately 5 seconds until the engine has developed enough oil pressure to close the oil pressure safety switch.
b.Ignition Switch (IGN) (see Figure 2.6)
The ignition switch is of the momentary type to be used in the OFF/ON/START positions. When held in the START (ignition) position, it energizes the starter motor solenoid, which in turn allows the starter motor to crank the engine. The switch is released to the RUN position once the engine has started.
c.Ignition Switch (IGN) (Auto Restart) (see Figure 2.7)
The ignition switch is of the maintained contact type to be used in the RUN/OFF positions. When switched to the RUN position, it energizes the control module, which in turn controls all functions of the generator set.
a.Intake Heater Timer (IHT) (If Equipped)
The intake heater timer continues to supply power to the intake heater for 3 minutes after initial start- up.
The Starter Timer limits the amount of time that the starter can be engaged to 15 seconds. If the starter is manually engaged for more than 15 seconds, power will be cut to the starter. Once power has been removed, the starter can again be engaged for up to 15 seconds.
Figure 2.6 Control Box Standard
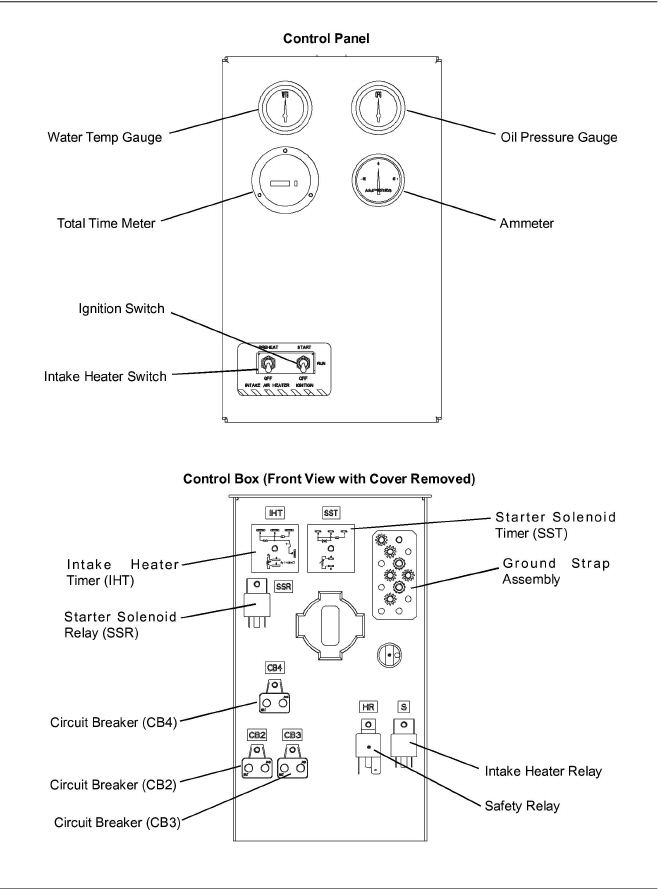
Figure 2.7 Control Box and Panel With Auto Restart
Indicator |
Preset Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Overspeed |
2100 RPM |
Overspeed is the point at which the unit will signal for shutdown. |
Crank Disconnect |
700 RPM |
Crank Disconnect is the point at which the Auto Restart module senses the engine has started and will disengage the starter. |
Shutdown Lockout Delay |
15 seconds |
The oil pressure and water temperature inputs are ignored during this 15 second delay (during startup). |
Intake Heater Delay |
30 seconds preheat 3 minutes post heat |
The delay is used during start up. The intake heater delay begins timing after the auto restart module signal is received. During the entire delay, the intake heater circuit will be energized, an indicator light will be illuminated, and an alarm will sound. When the delay expires, the unit will crank. |
Crank Attempts |
18 attempts |
A series of six attempts with three attempts in each series for a total of 18 attempts, refer to Table 2–3, Auto Restart Sequencing. |
Safety devices, such as circuit breakers, fuses, and safety switches, protect system components from damage.
The AC generator, solid state battery charger, fuel heater, high water temperature, safety relay, total time meter and intake heater are protected by circuit breakers. If a safety device opens and there is an interruption of electrical current, the electronic governor module will be de−energized, which will also de-energize the fuel solenoid, interrupt the fuel flow to the engine and stop the engine.
In units with auto restart, the engine, engine control devices, and engine monitoring devices are protected by the auto restart module, circuit breaker, low oil pressure switch, and high water temperature switch. These safety devices monitor system operating conditions and open a set of electrical contacts when an unsafe condition occurs. If a safety device opens and there is an interruption of electrical current, the electronic governor module will be de-energized, which will also de-energize the fuel solenoid, interrupt the fuel flow to the engine and stop the engine.
De-energizing the fuel solenoid shuts off the fuel supply to the engine; thus stopping the engine. Safety device specifications are provided in Table 2–4.
Bore /Stroke: |
3.26 in. (83 mm) / 4.03 in. (102.4 mm) |
|
Compression Ratio: |
22.0 to 1 |
|
Cylinders (Number): |
Four |
|
Displacement: |
135.2 cubic inches (22 lb cm3) |
|
Firing Order: |
1-3-4-2 |
|
Lubrication System: |
Oil Pressure Safety Switch Setting Opens |
18 psig (1.27 kg/cm2) |
Capacity |
Engine − 15.0 US quarts (14.2 liters), includes standard filter. |
|
Oil Level Indicator |
Dipstick in oil pan or fill cap NOTE: |
|
|
Lube Oil Viscosity |
Outdoor Temperature |
Fahrenheit: 0°F to 45°F Centigrade: -18°C to 7°C SAE: 10W30 or Mobile Delvac 1* |
||
Fahrenheit: 45°F and above Centigrade: 7°C and above SAE: 10W30 or 15W40 or Mobile Delvac 1* |
||
* Mobile Delvac 1, 5W-40 or 15W-40 is the only approved synthetic oil. |
||
Fuel and Fuel Heater Thermostat (FHT): |
Winter |
Diesel No. 2 with winter blends |
Summer |
Diesel No. 2 |
|
FHT |
||
Winter |
Close on temperature fall @ 45+ 6.5°F |
|
Summer |
Open on temperature rise @ 75 + 6.5°F |
|
Power Consumption: 150 Watts @ + 10% at 14 VDC |
||
- Diesel Fuel Specification Type and Sulfur Content % (ppm) used, must be compliant with all applicable emission regulations for the area in which the engine is operated. - Since KUBOTA diesel engines of less than 56 kW (75 hp) utilize EPA Tier 4 and Interim Tier 4 standards, the use of ultra low sulfur fuel is mandatory for these engines, when operated in US EPA regulated areas. Therefore, please use No.2−D S15 diesel fuel. Ultra Low Sulfur Diesel (ULSD) 15 ppm or 0.0015 wt.% |
||
Fuel Warmer: |
Coolant Temperature |
|
Intake Heater: |
Amperage - 42 amps at 12 VDC |
|
Resistance (cold) - Approx. 0.3 ohms |
||
Horsepower: |
24.8 HP @ 1800 RPM at sea level. (SAE J1995 Gross Power Rating) |
|
Cooling System: |
Capacity |
6 U.S. quarts (5.68 liters) - includes 1 quart (0.95 liter) in coolant recovery bottle. (Refer to Section 5.5.5) |
Anti-Freeze: Extended Life |
The cooling system is factory charged with a 50/50 mix of extended life coolant (ELC) and deionized water. This mixture provides protection to -34°F (-37°C). For replacement, with extended life coolant (ELC) meeting ASTM D4656 specification and deionized water. A 50/50 mix is recommended. Extended life coolant is red or orange in color. DO NOT mix with conventional coolant. |
|
Water Temperature Safety Switch Setting: |
||
Opens |
230 + 5°F (110 + 3°C) |
|
Resets |
200°F (93°C) - minimum |
|
Thermostat: |
||
Starts to open |
177 to 182°F (80 to 84°C) |
|
Fully open |
203°F (95°C) |
|
Lubrication System: |
Oil Pressure |
35 to 60 psig (3.3 to 5.2 kg/cm) |
Electrical: |
Generator |
400-500 VAC @ 60 hz 360-460 VAC @ 50 hz |