
Section 5
SERVICE AND PREVENTATIVE MAINTENANCE
This section covers service for the generator set and general engine service. Refer to the Kubota engine workshop manual (refer to Section 2.1) for other engine servicing.
Beware of moving poly V-belt and belt driven components.
5.2Preventative Maintenance Schedule
A tabular listing of the recommended preventative maintenance activities and schedule is provided in Table 5–1.
When replacing the battery, note if the unit was supplied with a mat in the battery tray. If so equipped, the mat must also be replaced.
Orient battery cables approximately as shown in Figure 5.1 and Figure 5.2. When installing cables to battery, ensure the cables are not touching anything, and are floating in free air.
Figure 5.1 Battery Cable Routing - Top View

Figure 5.2 Battery Cable Routing - Side View

PIDs prior to RG2059 are equipped with a battery charger mounted on the generator. If so equipped, when replacing the battery charger ensure the cables are NOT touching anything to prevent the wire chaffing with the following:
1.It is critical to maintain a 20° (+ 5 degrees) angle on the harness clamp. Refer to item b in Figure 5.3.
2.The positive and negative battery cables must be at a minimum distance, 0.25 in. (6.4 mm) from the battery charger and the battery charger mounting bracket. Refer to item a in Figure 5.3.
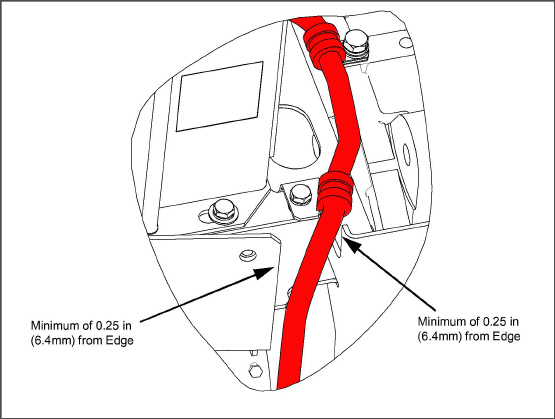
3.The harness must be at a minimum distance of 0.25 in. (6.4 mm) from the edges as shown in the Figure 5.4.
Figure 5.3 Battery Cable / Harness Clamp (PIDs prior to RG2059)
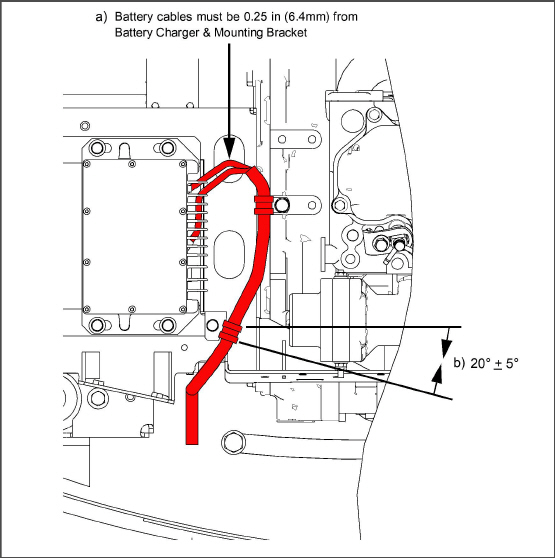
Figure 5.4 Battery Harness (PIDs prior to RG2059)
5.5Engine Service and Components
The unit is equipped with a mechanical fuel lift pump, mounted on the engine next to the injection pump. The fuel system is a closed circuit which will require bleeding if loss of fuel has occurred. To fill and bleed the system, do the following:
1.Turn bleed valve (Red, see Figure 2.4) counterclockwise until fully opened.
2.Turn the top of the hand priming pump counter-clockwise to unlock it, and then hand pump the manual plunger until a positive pressure (resistance) is felt. This will indicate fuel flow.
3.Depress and turn the top of the hand priming pump clockwise to lock in place.
4.Start engine. (Refer to Section 3.3).
5.When engine is running properly, turn bleed valve clockwise until fully closed.
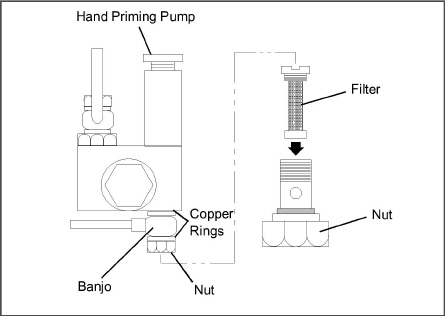
5.5.2Servicing Fuel Pump Internal Filter
The internal fuel filter may become plugged or restricted with foreign particles or wax, which can develop if the wrong grade of fuel is used or untreated fuel is used in cold weather, contaminating the fuel. If the internal filter is plugged, the engine will lose power. Therefore, the filter must be cleaned on a regular basis. The quality of the fuel will affect the filter cleaning schedule (refer to Section 5.2).
1.Turn nut counter-clockwise to loosen and remove
2.Remove banjo fitting and let it hang loose.
3.Turn filter counter-clockwise and remove. Check and clean.
4.To install, reverse steps a through c.
Figure 5.5 Mechanical fuel Pump
The fuel filter is located on the generator set unidrive assembly (see Figure 2.2). To replace the fuel filter, loosen and remove the filter housing. Lightly oil new gasket with lube oil and replace the filter.
If the generator set is equipped with the fuel filter bowl assembly, when replacing the fuel filter, a new fuel filter O-ring should be oiled and replaced, and then the clear bowl should also be tightened to 18 ft-lbs.
5.5.4In-Line Fuel Strainer (Option)
Loosen bowl by turning counter-clockwise. To renew, remove in-line fuel strainer, check and clean, and replace.
To ensure adequate cooling, the radiator must be clean, externally and internally. To service the cooling system, do the following:
1.Remove all foreign material from the radiator coil by reversing the normal air flow. Compressed air or water may be used as a cleaning agent. It may be necessary to use warm water mixed with any good commercial dishwasher detergent. Rinse coil(s) with fresh water if a detergent is used.
2.Drain coolant completely by opening drain-cock and removing radiator cap.
Never pour cold water into a hot engine.
3.Close drain-cock and fill system with clean, untreated water to which three to five percent of an alkaline base radiator cleaner should be added; six ounces (dry) = 151 grams to one gallon (3.8 liter) of water.
4.Run engine 6 to 12 hours and drain system while warm. Rinse system three times after it has cooled down. Refill system with water.
Use only ethylene glycol (anti-freeze with inhibitors) in system. Use of glycol by itself will damage the cooling system. (Refer to Section 2.11.)
5.Run engine to operating temperature. Drain system again and fill with treated water/anti-freeze. (See above Caution note and refer to Section 2.11.)
The oil filter is located near the radiator fan (see Figure 2.5).
1.After warming up the engine, stop engine, remove drain plug from oil reservoir and drain engine lube oil.
2.Replace filters. Lightly oil gasket on filter before installing.
3.Add lube oil (Refer to Section 2.3.4).
4.Warm up engine and check for leaks.
5.5.7Servicing Low Oil Pressure Switch
1.Remove harness connection from low oil pressure switch (LOP).
2.Remove pressure switch from engine.
3.Apply Teflon thread sealer to threads of new low oil pressure switch.
4.Install new low oil pressure switch.
5.Reconnect harness connection to low oil pressure switch.
The engine speed is electronically controlled.
Do not attempt to adjust engine speed.
5.5.9Replacing the Engine Speed Sensor
1.Disconnect the plug to the sensor.
2.Remove the bolt securing the sensor to the housing.
3.Remove the sensor from the housing.
4.Clean the recess in the housing to ensure that the sensor seats properly when re-installed.
5.Re-install the sensor, replace the securing bolt and connect the plug to the sensor.
Beware of moving poly V-belt and belt driven components.
Beware of pinch points.
A frayed, cracked or worn poly V-belt must be replaced. After installing a new belt, check the adjustment after running the unit for three or four hours. This will allow for the initial stretch, which is common on new belts. Once this initial stretch has taken place, the belt should be checked at regular intervals.
The poly V-belt is driven by a sheave on the engine crankshaft. Its two functions are to:
•drive the radiator fan
•drive the water pump
To replace the poly V-belt, perform the following steps:
1.Using the proper size socket, slowly rotate the crank on the crank pulley nut. At the same time, use a flat, blunt object to guide the belt off the crank pulley towards radiator. Be careful not to damage grooves on the pulley.
2.Replace the poly V-Belt by positioning the belt on the water pump pulley, and while rotating the engine (as in step a.), use a flat, blunt object to guide the belt onto the crank pulley. Be careful not to damage grooves on the pulley or belt.
The dry element engine air cleaner uses a dry element filter (see Figure 5.6) to filter the engine intake air. The oil bath air cleaner option uses an oil cup instead of the standard dry element filter (see Figure 5.7).
The engine air cleaner should be inspected regularly for leaks, (see Figure 2.1). A damaged air cleaner or hose can seriously affect the performance and life of the engine. The air cleaner is designed to effectively remove contaminants from the air stream entering the engine. An excessive accumulation of contaminants in the air cleaner will impair its operation. Therefore, a service schedule must be set up and followed.
1.Check all connections for mechanical tightness. Be sure the air cleaner outlet pipe is not fractured.
2.In case of leakage, if adjustment does not correct the problem, replace necessary parts or gaskets. Swollen or distorted gaskets must always be replaced.
The air filter indicator, used with the dry element filter, is mounted on the air filter body. Its function is to indicate when the air cleaner dry element needs to be replaced. In operation: When a plugged air cleaner decreases intake manifold pressure to 500 mm (20”) WG, the indicator moves to the red line. The air cleaner element should be replaced and the indicator reset by pressing the reset button.
Air Cleaner, Dry Element Service Procedure
1.Stop the engine and open the cap clamps (see Figure 5.6) to remove air cleaner bottom cap.
2.Remove the air filter element from the air cleaner body.
3.Install the new element, secure the bottom cap with the cap clamps.
Figure 5.6 Air Cleaner, Dry Element
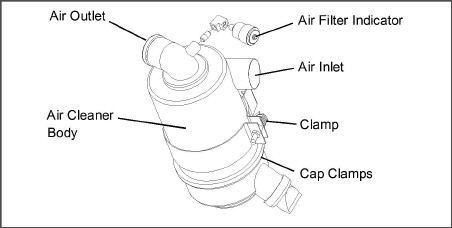
When reassembling the Air Cleaner, make sure the Clamp Bolt faces out, away from the fuel filter. If the Clamp Bolt is assembled facing in, it can contact the fuel filter and cause excessive wear.
Air Cleaner, Oil Bath Service Procedure
The oil cup should be inspected during pretrip, before each trip. Never allow more than 1/2 inch (12.7 mm) of dirt deposit in the cup. More than 1/2 inch accumulation could result in oil and dirt carrying over into the engine, causing accelerated engine wear. Heavily contaminated oil will not allow the air cleaner to function properly.
Always cover the engine inlet tube while the air cleaner is being serviced.
1.Stop the engine and remove the oil cup from the air cleaner. Dispose of oil in an environmentally safe manner.
2.Remove the inner oil cup from the oil cup and clean both cups.
3.Reassemble and fill both oil cups to the indicated level with oil specified in Section 2.11.
Do not underfill or overfill the oil bath cups. Overfilling cups causes loss of capacity; underfilling cups causes lack of filtering efficiency.
Figure 5.7 Air Cleaner, Oil Bath

The air cleaner body should be inspected each time the oil cup is serviced. If there is any sign of contaminant buildup or plugging, the air cleaner body should be removed and back flushed.
At least once a year, or at regular engine service intervals, remove the entire air cleaner and perform the following cleaning procedure:
1.Remove oil cup. Check and clean center tube.
Do not use gasoline to clean air cleaner parts.
2.Pump solvent through the air outlet with sufficient force and volume to produce a hard, even stream out of the bottom of the body assembly. Reverse flush until all foreign material is removed.
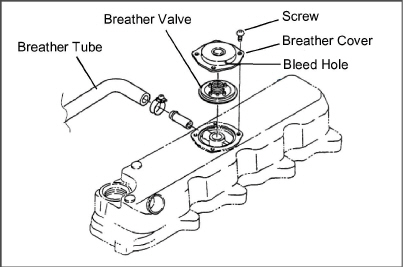
5.5.12Engine Crankcase Breather
The engine uses a closed type breather with the breather line attached to the cylinder head cover (see Figure 5.8). It is not necessary to disassemble valve style elements for cleaning. However, the bleed hole should be checked to ensure it is free of obstruction. Check once a year or at every 4000 hours maintenance interval (whichever comes first).
Figure 5.8 Engine Crankcase Breather
1.Disconnect the lead from the heater terminal (positive).
2.Measure the resistance between the heater positive terminal and the heater body.
3.If the resistance is infinity or significantly different than the specification, resistance (cold) 0.3 ohms, replace the heater.

1.Remove harness connection from heater.
2.Remove intake transition mounting hardware.
3.Remove intake transition, heater and both gaskets.
4.Clean old gasket material off the transition and manifold mounting services.
5.Install new heater with a new gasket on either side.
6.Assemble transition to heater and torque mounting hardware (refer to engine manual for torque values).
7.Reconnect harness to heater connection point.
8.Coat stud on heater with protective coating.
1.Remove control box cover.
2.Remove all connections going to heater switch (HS).
3.Remove heater switch from control box.
4.Install new heater switch.
5.Reconnect wire harness connections to switch.
6.Confirm wires are connected to correct terminals.
7.Reinstall control box cover.
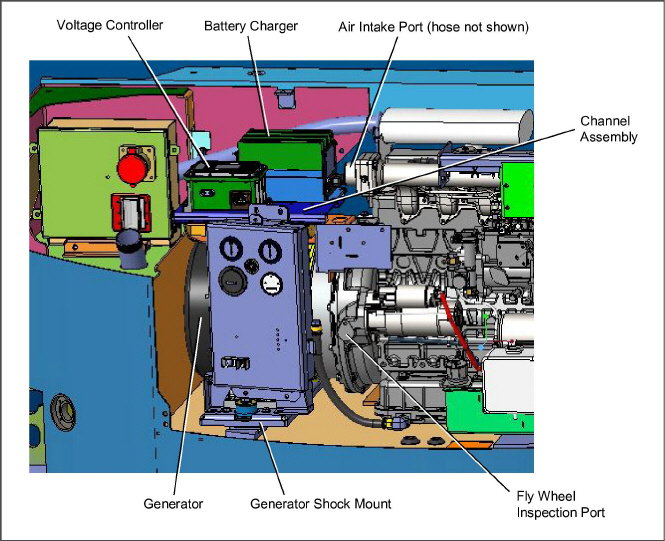
5.6Servicing the Alternating Current Generator
5.6.1Generator Removal and Installation
The only serviceable parts on the Generator are the Drive Gear (metal), Key, Fan, and Fan Cover. If there is a problem with the Generator, it should be replaced using the following procedure:
For additional torque values refer to paragraph Figure 5.17.
1.Remove covers from the frame of generator set.
2.Disconnect the battery.
Observe proper polarity when installing the battery or connecting a battery charger, the negative battery terminal must be grounded. Reverse polarity may damage the charging system. When charging the battery in unit, isolate the battery by disconnecting the negative battery terminal first, then the positive. Once the battery has been charged, connect the positive battery terminal first, then the negative.
3.Remove the 1/4” bolts/washers (4) that secure the voltage controller to the channel assembly. Disconnect the voltage controller wires and remove the voltage controller from the unit.
4.Remove the top plate of the battery charger from the channel assembly.
This step is only applicable for PIDs RG2059 and higher.
5.Remove the 1/4” bolts/washers (4) that secure the battery charger to the channel assembly. Disconnect the battery charger wires and remove the battery charger from the unit.
6.Remove the bolts/washers (6) that secure the receptacle box to the unit.
7.Un-tape the wire harness and cut the wires (7) that connect the receptacle box to the generator. Make sure to cut the wires on the receptacle box side of the current butt splices. Wire-tie the receptacle box to the frame so that it does not inadvertently fall, leaving the receptacle box hanging by the cables.
8.Loosen the intake air hose clamp and remove the intake air hose from the intake port to the engine.
9.Remove the bolts that secure the control box and move the control box out of the way. Wire-tie the control box to the frame so it does not inadvertently fall, leaving the control box hanging by the cables.
10.Remove the remaining channel assembly bolts/washers at the top of the generator (2 bolts) and at the front of the generator (2 bolts). The channel assembly bolts at the front of the generator are also generator mounting bolts.
11.Remove the bolts/washers (2) that secure the generator support plate to the two generator shock mounts.
12.Remove the bolt/washer (1) that secures the snubber shock mount to the frame.
13.Remove the bolt/washer (1) that secures the ground wire to the generator.
14.Back off (about 1”), but do not remove the engine shock mount bolts. This will allow the engine/generator to be slightly lifted off of the unit frame.
The generator/engine must be slightly lifted off of the unit frame in order to provide enough clearance for the generator support plate to slide back, away from the engine.
15.Using lifting lugs on the top of the generator, lift the generator/engine several inches so that the generator support plate will clear the unit frame allowing the entire generator assembly to be removed.
16.Place several support beams under the engine, and then lower the generator/engine onto the beams. Make sure that the generator support plate is still lifted high enough to allow the generator assembly to be moved back, away from the engine.
17.Starting with the lower bolts, remove the remaining bolts/washers (10) that secure the generator to the engine.
Although the generator drive gear and fly wheel adapter plate will normally keep the generator coupled to the engine, even without the bolts, it is safest to remove the lower generator bolts first, in case the generator shifts and falls during bolt removal.
18.Lift the generator assembly (generator & support plate) up, and away from the engine, lower it onto a stable work surface.
Inspect the generator drive gear, bolt, and key as they will have to be removed from the old generator and installed onto the new generator; replace these components if they are worn or damaged.
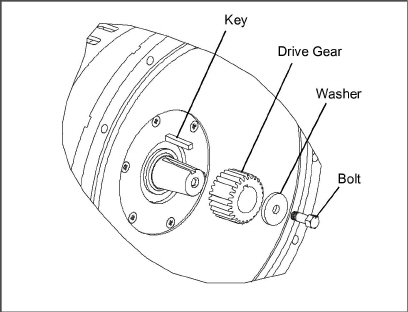
19.Remove the generator drive gear bolt/washer.
20.Use a gear puller to remove the drive gear and key from the generator drive shaft.
21.Place the key into the slot on the drive shaft of the new generator, and install the drive gear over the drive shaft and key.
22.Replace and torque the generator drive gear bolt/washer, torque to 28 + 2 ft-lbs. In order to torque generator drive gear bolt you will have to use a strap wrench or similar device to secure the gear while you torque the bolt.
23.Remove the generator support plate from the old generator, and install it onto the new generator.
24.With the drive gear and support plate installed on the new generator, lift and position the generator so that the generator mounting holes (12) are lined up with the engine mounting holes.
25.Insert two generator alignment bolts (2 1/2”) to temporarily align/secure the generator to the engine. Tighten the bolts enough so that the metal gear on the generator is touching the blue drive gear on the engine. Do not over tighten the alignment bolts, as they will bottom out on the engine bell housing.
In order to match up the teeth of the generator drive gear with the teeth of the fly wheel adaptor plate, the fly wheel will need to be rotated by hand.
26.Remove the cover of the fly wheel inspection port. Using a long flat head screwdriver inserted into the fly wheel inspection port, you will be able to slowly rotate the teeth of the fly wheel.
27.With the generator drive gear pressed against the coupling on the fly wheel adaptor plate, use the screwdriver to slowly rotate the fly wheel. Use a flashlight to observe the generator drive gear as you rotate the fly wheel. Once the generator drive gear starts to rotate with the fly wheel, it indicates that the teeth of the generator drive gear have matched up with the mating gear of the fly wheel adaptor plate.
28.Once the teeth of the generator drive gear teeth have lined up with the fly wheel adapter plate, push the generator in to fully seat the drive gear into the mating gear on the fly wheel adaptor plate.
29.Close and secure the fly wheel inspection port.
30.With the generator drive gear seated into the fly wheel adaptor plate, the alignment bolts (2) can be removed, and the generator mounting bolts (10) can be reinstalled, torque to 25 ft-lbs. Do not install the bolts (2) that secure the channel assembly to the generator. Install several mounting bolts to secure the generator before removing the alignment bolts.
Although the drive gear and mating surface of the generator will generally keep the generator coupled to the engine, even with all of the bolts removed, it is safest to start installation of the top generator bolts first, just in case the generator shifts and falls.
31.With all of the generator mounting bolts secured, use the lift to raise the generator/engine in order to remove the support blocks under the engine.
32.Lower the generator/engine so that the generator support plate holes line up with the shock mount holes. Install the bolts/washers (2) and torque to 75 ft-lbs.
33.Replace the bolt/washer (1) that secures the ground wire to the generator.
34.Tighten the engine shock mount bolts to 90 ft-lbs.
35.Replace the bolt/washer (1) that secures the snubber shock mount to the frame, torque to 75 ft-lbs.
36.Cut the wire-tie that is supporting the receptacle box and re-secure the receptacle box to the unit frame using bolts/washers (6). Make sure the receptacle wires are in a good position to splice with the generator wires.
37.Place two pieces of heat shrink (1 large, 1 small) over each receptacle box wire.
38.Connect and butt splice the receptacle box wires with the new generator wires.
39.For each of the wires, shrink the small heat shrink first, and then the large heat shrink to ensure a water tight seal.
40.Replace the channel assembly bolts/washers on to the top of the generator (2) and at the front of the generator (2). The channel assembly bolts at the front of the generator are also generator mounting bolts, torque to 25 ft-lbs.
41.Re-install the top plate of the batter charger.
This step is only applicable for PIDs RG2059 and higher.
42.Replace the battery charger cables and secure the battery charger to the channel assembly using the 1/4” bolts/washers (4). Refer to Figure 5.12, Figure 5.13
Observe proper polarity when installing the battery or connecting a battery charger, the negative battery terminal must be grounded. Reverse polarity may damage the charging system. When charging the battery in unit, isolate the battery by disconnecting the negative battery terminal first, then the positive. Once the battery has been charged, connect the positive battery terminal first, then the negative.
Figure 5.12 Battery Charger (PIDs Prior to RG2059)

Figure 5.13 Battery Charger (PIDs RG2059 and Up)
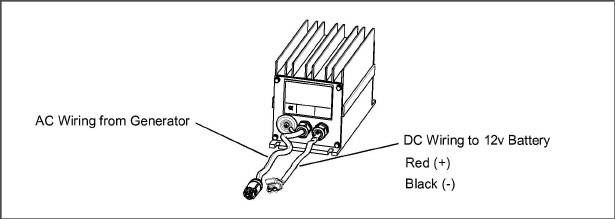
43.Replace the voltage controller cables and secure the voltage controller to the channel assembly using the 1/4” bolts/washers (4). Make sure to also secure the two wire harness clamps using the left side voltage controller mounting bolts.
44.Replace the intake air hose and clamp the air intake hose to the intake port.
45.Re-connect the battery.
46.Replace and secure the unit cover.
5.7General Generator Set Maintenance
5.7.1Maintenance of Painted Surfaces
The unit is protected against the corrosive atmosphere in which it normally operates by a special paint system. However, should the paint system be damaged, the base metal can corrode. If the paint system is scratched or damaged, do the following:
1.Clean area to bare metal using a wire brush, emery paper or equivalent cleaning method.
2.Immediately following cleaning, spray or brush on a zinc rich primer.
3.After the primer has dried, spray or brush on finish coat of paint to match original unit color.
5.7.2Checking and Replacing Shockmounts
Replacement Criteria
Continued operation with failed shockmounts may result in engine or generator damage.
When a shockmount has been cut, split, abraded or has flared due to normal deterioration, it must be replaced. Damage to the mounts may not be visible when installed and under load from the component. To correctly inspect shockmounts, they must be removed.
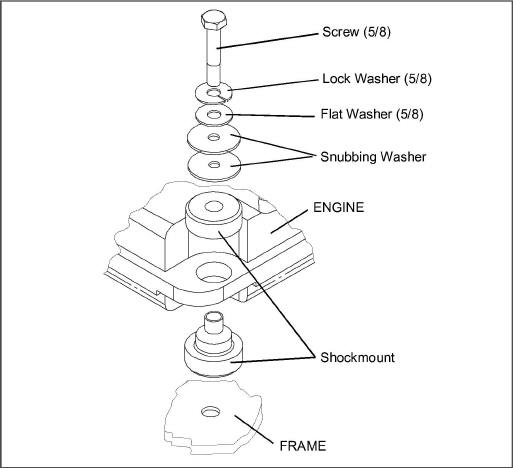
Engine Shockmount Replacement
Refer to Section 5.8 for torque values.
1.Use the two lift eyes to lift and support the engine.
2.Remove snubber hardware as shown in Figure 5.14.
3.Remove all hardware as shown in Figure 5.15.
4.Raise the engine just enough to remove the shockmounts.
5.Inspect shockmounts and replace if required.
6.Lower the engine enough to assemble hardware as shown and torque per Section 5.8.
7.Replace snubber hardware as shown in Figure 5.14.
8.Remove chains from the lift eyes.
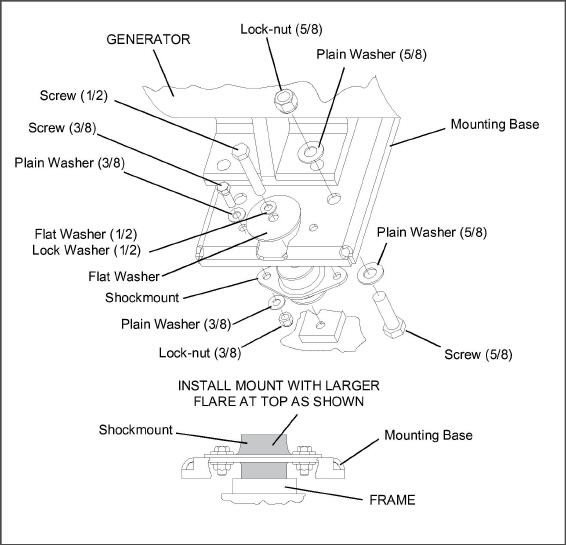
Generator Shockmount Replacement
1.Use the two lift eyes to lift and support the engine.
2.Remove snubber hardware as shown in Figure 5.14.
3.Remove shockmount hardware, Figure 5.16.
4.Raise the generator just enough to remove the shockmounts.
5.Inspect and if required, install new shockmounts.
6.Lower the engine enough to assemble hardware as shown and torque. Refer to Figure 5.8 for torque values.
7.Replace snubber hardware as shown in Figure 5.14.
8.Remove chains from the lift eyes.

Figure 5.15 Engine Shockmounts
5.8Unidrive Torque Requirements
Extensive damage may occur if the proper hardware is not used and/or proper procedures are not followed when working with the unidrive assembly. Periodic inspection of hardware and bolt torque is recommended to ensure the integrity of the unidrive.
Torque value and hardware requirements for unidrive assembly are provided in Figure 5.17.
Figure 5.16 Generator Shockmounts
SST is an abbreviation
for 300 Series Corrosion Resistant Steel.
Loctite #242 or an equivalent product should be used on ALL hardware shown
in Figure
5.17.
Figure 5.17 Unidrive Torque Requirements

Units have mineral oil installed from the factory. Change lubricating oil and filters after the first 2000 hours of service or at the end of the first year, whichever comes first.
Oil changes after the first 2000 hour service, or 1 year:
- If using mineral oil, oil changes should continue every 2000 hours of service or every 1 year, whichever comes first.
- If using specified synthetic lubricating oil and OEM extended life oil filter, oil changes should be completed every 4000 hours of service, or every two years, whichever comes first.
1 Pre-trip maintenance checks should be carried out prior to any use of the unit (1-15 and 31-36).
2 2000 hour maintenance checks should be carried out annually or every 2000 hours, whichever comes first.
3 4000 hour maintenance checks should be carried out every two years or every 4000 hours, whichever comes first