Section 3
3.1.1Refrigeration Unit - Front Section
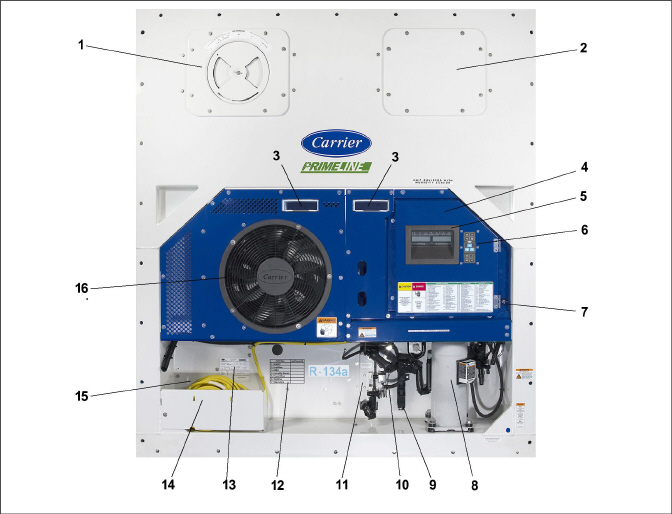
The unit is designed so that the majority of the components are accessible from the front, see Figure 3.1. The unit model number, serial number and parts identification number can be found on the unit nameplate on the back wall of the condenser section.
Figure 3.1 Refrigeration Unit - Front Section

1)Upper Fresh Air Makeup Vent Panel. Located inside are: Evaporator Fan #2, Defrost Temperature Sensor (DTS)
2)Access Panel. Located inside are: Evaporator Fan #1, Electronic Expansion Valve (EEV), Heat Termination Thermostat (HTT)
9)Access Panel for Supply Temperature Sensor / Supply Recorder Sensor (STS / SRS)
10)Ambient Temperature Sensor (AMBS)
13)Unit Nameplate (serial number, model number and PID number)
15)Autotransformer location (if equipped)
- - - - -
The compressor, see Figure 3.2, receives refrigerant vapor from the evaporator and compresses it to a high pressure, high temperature gas before directing it to the condenser. The compressor section, see Figure 3.3, includes the following components: compressor, digital unloader valve (DUV), high pressure switch (HPS), discharge pressure transducer (DPT), evaporator pressure transducer (EPT) and the suction pressure transducer (SPT).

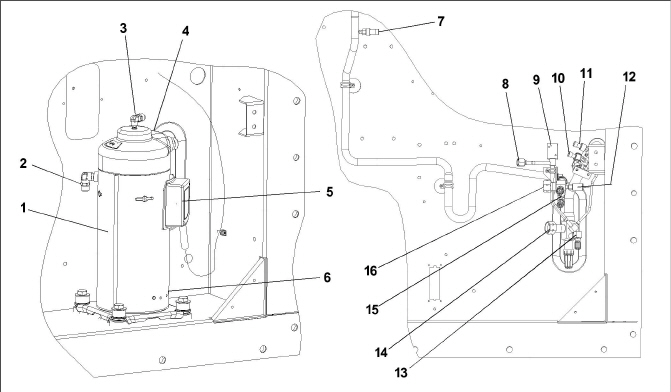
3)Digital Unloader Valve (DUV) connection
4)Compressor Discharge Temperature Sensor (CPDS) location
7)Discharge Pressure Transducer (DPT)
8)Digital Unloader Valve (DUV) connection
9)Digital Unloader Valve (DUV)
10)Suction Pressure Transducer (SPT)
11)Evaporator Pressure Transducer (EPT)
- - - - -
3.1.3Air-Cooled Condenser Section
The air-cooled condenser removes latent heat from the refrigerant gas by using a condenser fan, see Figure 3.4, to blow air across the condenser coil fins and tubes to cool the gas to saturation temperature. The condenser fan pulls air from around the coil and discharges it horizontally through the condenser fan grille.
The air-cooled condenser section consists of: the condenser fan, condenser coil, receiver with sight glass / moisture indicator / fusible plug, liquid line service valve, filter drier, economizer, economizer expansion valve (EXV) and economizer solenoid valve (ESV). See Figure 3.5, Figure 3.6

Figure 3.5 Condenser Section for PIDs < NT3100 (Steel Receiver)
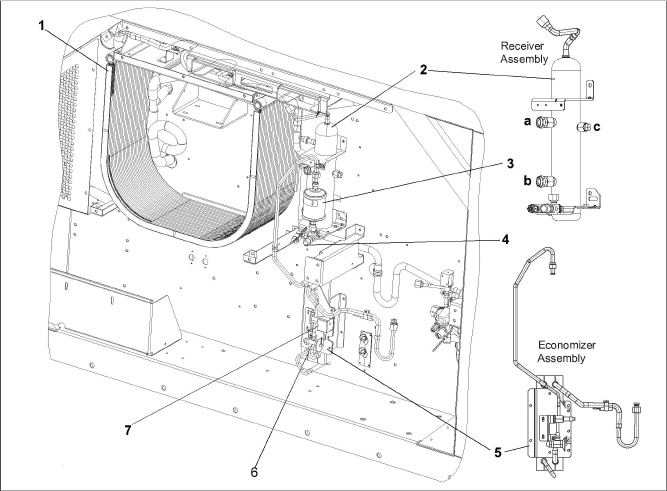
1)Condenser Coil, Microchannel Heat Exchanger (MCHE)
2)Receiver (steel) with: a) sight glass, b) moisture indicator and c) fusible plug
4)Service Access Valve
6)Economizer Expansion Valve (EXV)
7)Economizer Solenoid Valve (ESV)
- - - - -
Figure 3.6 Condenser Section for PIDs > NT3100 (Aluminum Receiver)
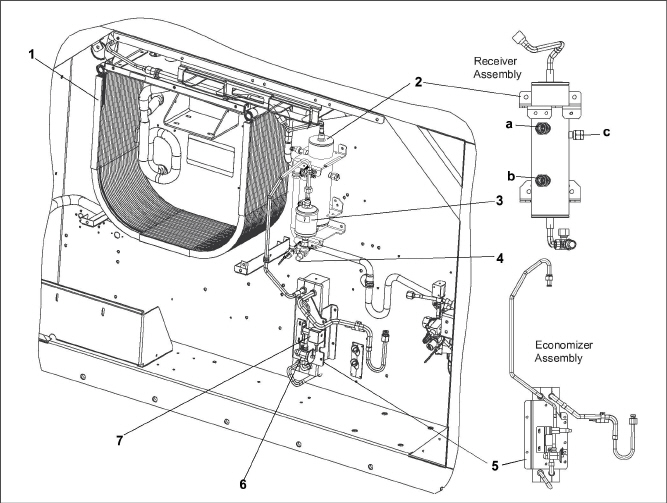
1)Condenser Coil, Microchannel Heat Exchanger (MCHE)
2)Receiver
(aluminum) with: a) sight glass,
b) moisture indicator and c) fusible plug
6)Economizer Solenoid Valve (ESV)
7)Economizer Expansion Valve (EXV)
- - - - -
3.1.4Water-Cooled Condenser Section
The unit may contain a brazed plate water-cooled condenser (WCC) installed as an option. When operating on the water-cooled condenser, the condenser fan is deactivated by a water pressure switch or condenser fan switch.
The WCC, see Figure 3.7, consists of a brazed plate water-cooled condenser, water couplings and a water pressure switch. The receiver is retained in this configuration and the brazed plate heat exchanger is placed between the air-cooled condenser and the receiver.
Figure 3.7 Brazed Plate Water-Cooled Condenser
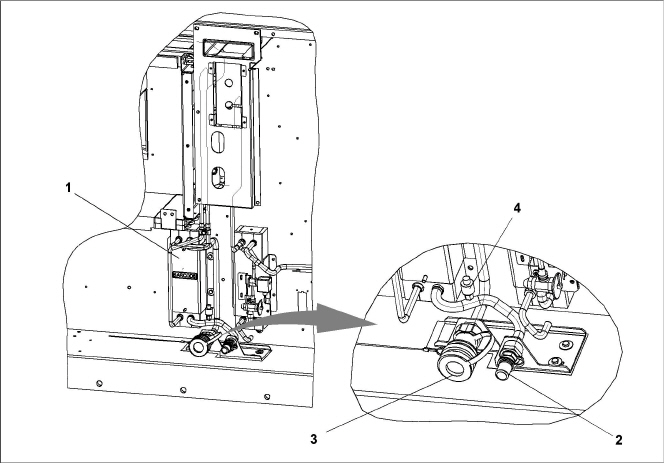
1)Water-Cooled Condenser (WCC)
3)Self Draining Coupling (Water Out)
- - - - -
The function of the upper fresh air makeup vent, see Figure 3.8, is to provide ventilation for commodities that require fresh air circulation. A manually operated venting system is located in the upper left access panel.

The evaporator section is shown in Figure 3.9. The evaporator fans circulate air through the container by pulling it into the top of the unit, directing it through the evaporator coil to be heated or cooled, and discharging it at the bottom.
Most evaporator components are accessible by removing the upper rear panel or by removing the evaporator fan access panels.
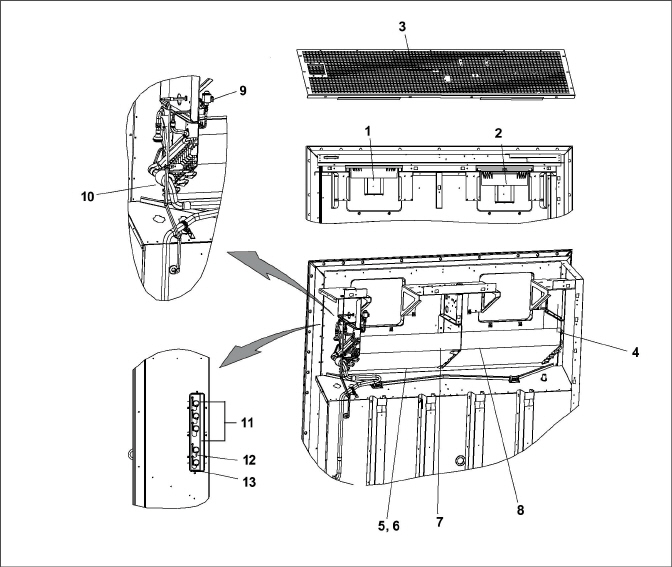
1)Evaporator Fan and Motor (EM1)
2)Evaporator Fan and Motor (EM2)
3)Return Temperature Sensor (RTS) / Return Recorder Sensor (RRS)
6)Heaters**
7)Heat Termination Thermostat (HTT)**
8)Defrost Temperature Sensor (DTS)**
9)Electronic Expansion Valve (EEV)
10)Evaporator Temperature Sensors (ETS1 / ETS2)
11)USDA Probe Receptacles (PR1, PR2, PR3)
12)Cargo Probe Receptacle (PR4)
13)Interrogator Connector Rear (ICR)
- - - - -
** general location, not shown in figure.
The control box, see Figure 3.10, includes the manual operation switches, circuit breaker (CB-1), compressor, fan and heater contactors, control power transformer, transformer AC line filter, fuses, keypad, display module, current sensor module, and the controller module.
Figure 3.10 Control Box Section
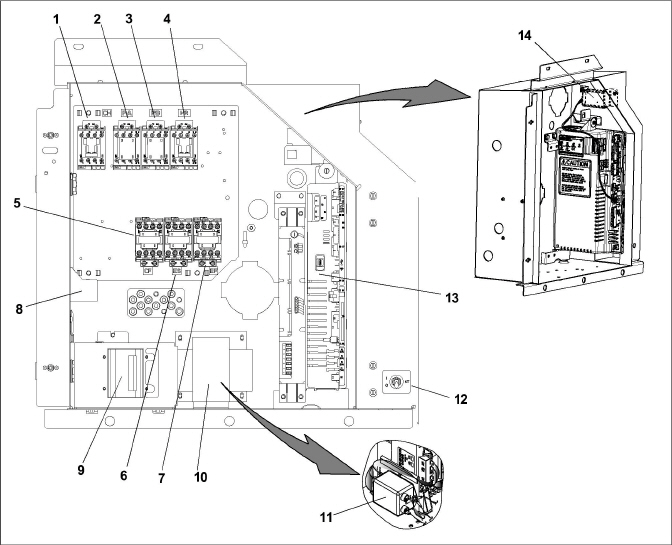
2)Compressor Phase A Contactor (PA)
3)Compressor Phase B Contactor (PB)
5)Condenser Fan Contactor (CF)
6)Low Speed Evaporator Fan Contactor (ES)
7)High Speed Evaporator Fan Contactor (EF)
13)Controller / DataCORDER Module
14)Controller Battery Pack and Battery
- - - - -
3.4Safety and Protective Devices
Unit components are protected from damage by safety and protective devices listed in Table 3–3. These devices monitor the unit operating conditions and open a set of electrical contacts when an unsafe condition occurs.
Open safety switch contacts on either or both of devices IP-CP or HPS will shut down the compressor.
Open safety switch contacts on device IP-CM will shut down the condenser fan motor.
The entire refrigeration unit will shut down if one of the following safety devices open: (a) circuit breaker(s); (b) fuse (F3 / F4, 7.5A); or (c) evaporator fan motor internal protector(s) - (IP).
See Figure 3.11 for Circuit Diagram of Standard Operation
See Figure 3.13 for Circuit Diagram of Standard Operation with Water-Cooled Condenser
Starting at the compressor, the suction gas is compressed to a higher pressure and temperature.
The refrigerant gas flows through the discharge line and continues into the air-cooled condenser. When operating with the air-cooled condenser active, air flowing across the coil fins and tubes cools the gas to saturation temperature. By removing latent heat, the gas condenses to a high pressure / high temperature liquid and flows to the receiver, which stores the additional charge necessary for low temperature operation.
When operating with the water-cooled condenser active, the refrigerant gas passes through the air-cooled condenser and enters the water-cooled condenser shell. The water flowing inside the tubing cools the gas to saturation temperature in the same manner as the air passing over the air-cooled condenser. The refrigerant condenses on the outside of the tubes and exits as a high temperature liquid. The water-cooled condenser also acts as a receiver, storing refrigerant for low temperature operation.
The liquid refrigerant continues through the liquid line, the filter drier (which keeps refrigerant clean and dry) and the economizer (not active during standard operation) to the electronic expansion valve (EEV).
As the liquid refrigerant passes through the variable orifice of the EEV, the pressure drops to suction pressure. In this process some of the liquid vaporizes to a gas (flash gas), removing heat from the remaining liquid. The liquid exits as a low pressure, low temperature, saturated mix. Heat is then absorbed from the return air by the balance of the liquid, causing it to vaporize in the evaporator coil. The vapor then flows through the suction tube back to the compressor.
On systems fitted with a water pressure switch, the condenser fan will be off when there is sufficient pressure to open the switch. If water pressure drops below the switch cut out setting, the condenser fan will automatically start.
During the standard mode of operation, the normally closed digital unloader valve (DUV) controls the system refrigerant flow and capacity by loading and unloading the compressor in frequent discrete time intervals. If the system capacity has been decreased to the lowest allowable capacity with the DUV, the unit will enter a trim heat mode of operation, during which the controller will pulse the evaporator heaters in sequence with the compressor digital signal in order to absorb the excess capacity.
See Figure 3.12 for Circuit Diagram of Economized Operation
In economized operation, the frozen and pull down capacity of the unit is increased by sub-cooling the liquid refrigerant entering the electronic expansion valve (EEV). Overall efficiency is increased because the gas leaving the economizer enters the compressor at a higher pressure, therefore requiring less energy to compress it to the required condensing conditions.
Liquid refrigerant for use in the economizer circuit is taken from the main liquid line as it leaves the filter drier. The flow is activated when the controller energizes the economizer solenoid valve (ESV).
The liquid refrigerant flows through the ESV to the expansion valve internal passages, absorbing heat from the liquid refrigerant flowing to the electronic expansion valve (EEV). The resultant “medium” temperature / pressure gas enters the compressor at the economizer port fitting.
When the control air temperature falls to 2.0°C (3.6°F) above setpoint, the DUV unloads the compressor’s scroll and begins to reduce the capacity of the unit. Percentage of the unit capacity is accessed through code select 01 (Cd01). For example, if Cd01 displays 70, it indicates that the compressor is operating unloaded with the DUV engaged 30% of the time.
3.5.3Electronic Expansion Valve (EEV)
The microprocessor controls the superheat leaving the evaporator via the electronic expansion valve (EEV), based on inputs from the evaporator pressure transducer (EPT). The microprocessor transmits electronic pulses to the EEV stepper motor, which opens or closes the valve orifice to maintain the superheat setpoint.
Figure 3.11 Refrigeration Circuit Diagram - Standard Operation
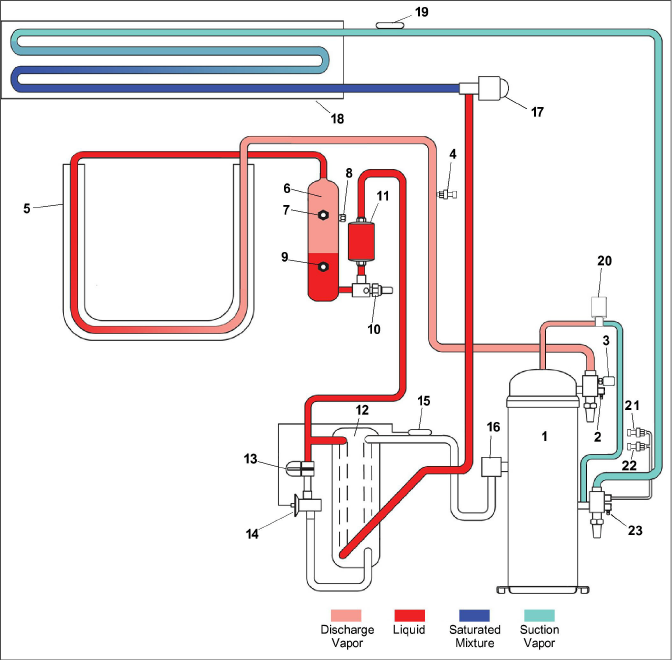
3)High Pressure Switch (HPS)
4)Discharge Pressure Transducer (DPT)
9)Receiver Liquid Level / Moisture Indicator
13)Economizer Solenoid Valve (ESV)
14)Economizer Expansion Valve (EXV)
15)Economizer Expansion Valve (EXV) Sensing Bulb
17)Electronic Expansion Valve (EEV)
19)Evaporator Temperature Sensor (ETS1 / ETS2)
20)Digital Unloader Valve (DUV)
21)Evaporator Pressure Transducer (EPT)
22)Suction Pressure Transducer (SPT)
- - - - -
Figure 3.12 Refrigeration Circuit Diagram - Economized Operation
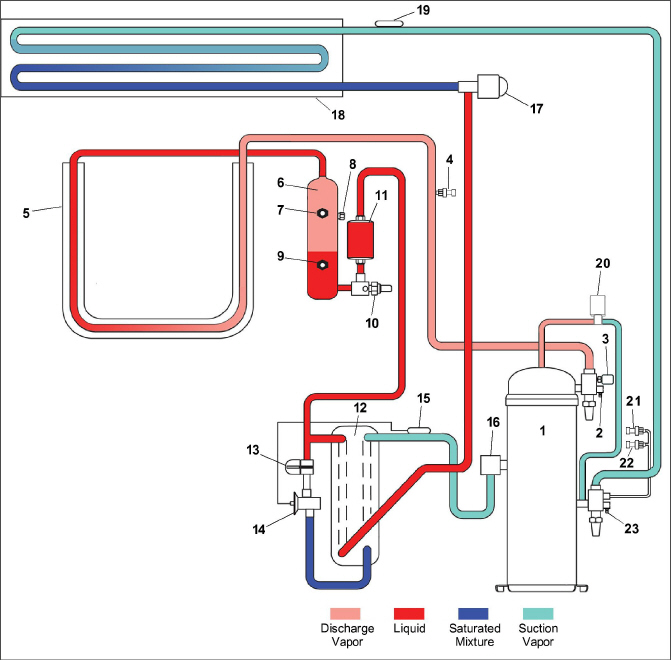
3)High Pressure Switch (HPS)
4)Discharge Pressure Transducer (DPT)
9)Receiver Liquid Level / Moisture Indicator
13)Economizer Solenoid Valve (ESV)
14)Economizer Expansion Valve (EXV)
15)Economizer Expansion Valve (EXV) Sensing Bulb
17)Electronic Expansion Valve (EEV)
19)Evaporator Temperature Sensor (ETS1 / ETS2)
20)Digital Unloader Valve (DUV)
21)Evaporator Pressure Transducer (EPT)
22)Suction Pressure Transducer (SPT)
- - - - -
Figure 3.13 Refrigeration Circuit Diagram - Water-Cooled Condenser
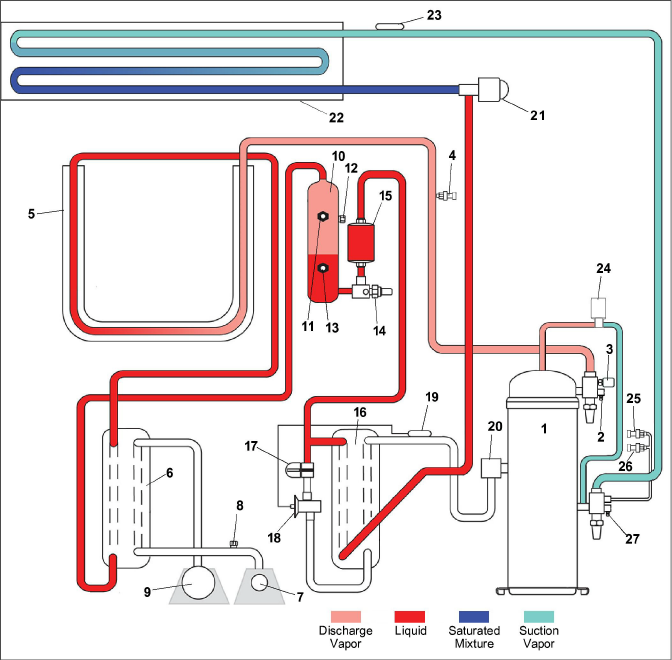
3)High Pressure Switch (HPS)
4)Discharge Pressure Transducer (DPT)
13)Receiver Sight Glass / Moisture Indicator
17)Economizer Solenoid Valve (ESV)
18)Economizer Expansion Valve (EXV)
19)Economizer Expansion Valve (EXV) Sensing Bulb
21)Electronic Expansion Valve (EEV)
23)Evaporator Temperature Sensor (ETS1 / ETS2)
24)Digital Unloader Valve (DUV)
25)Evaporator Pressure Transducer (EPT)
26)Suction Pressure Transducer (SPT)
- - - - -