Section 3
3.1.1Refrigeration Unit − Front Section
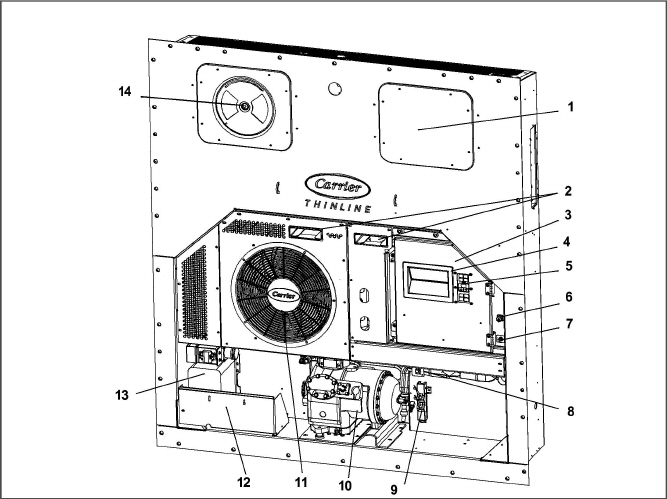
The unit is designed so that the majority of the components are accessible from the front (see Figure 3.1). The unit model number, serial number, and parts identification number can be found on the serial plate to the left of the compressor.
The function of the upper or lower makeup air vent is to provide ventilation for commodities that require fresh air circulation. A manually operated venting system is located in the upper left access panel. The optional eAutoFresh vent system is to moderate the atmospheric level in the container in response to cargo respiration. When transporting frozen cargo loads the vent will be closed. The upper left access panel contains the vent slide and motor assembly. It may be removed to allow entry into the evaporator section where the CO2 sensor and drive pack are located.
Figure 3.1 Refrigeration Unit - Front Section

1.Access Panel (Evap Fan #1) / TXV / HTT
6.Remote Monitoring Receptacle
9.Return Temperature Supply/Recorder Sensor Assembly (RTS/RRS)
12.Power Cables and Plug (Location)
14.Upper Fresh Air Makeup Vent
- - - - -
The evaporator section (Figure 2-2) contains the supply temperature sensor, humidity sensor, thermostatic expansion valve, dual-speed evaporator fans (EM1 and EM2), evaporator coil and heaters, defrost temperature sensor, heat termination thermostat, and heat exchanger.
The evaporator fans circulate air through the container by pulling it from the bottom of the unit, directing it through the evaporator coil where it is heated or cooled, and discharging it at the top.
The evaporator components are accessible by removing the upper rear panel (as shown in Figure 3.2).
Figure 3.2 Evaporator Section - Units with Center Access Panel
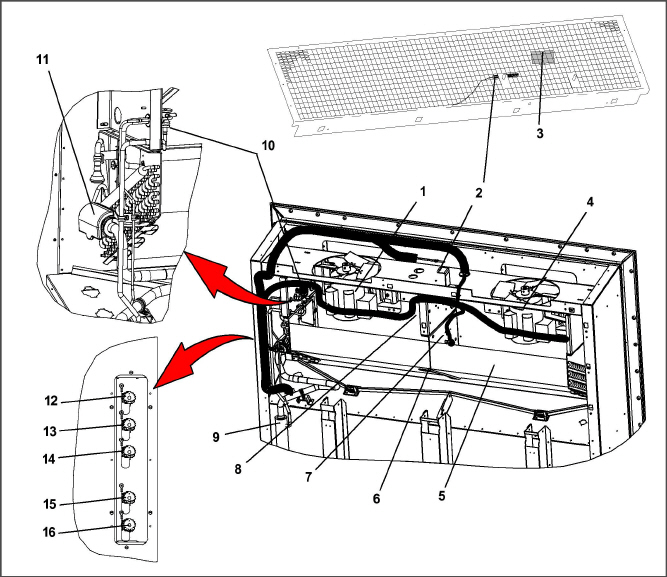
2.Supply Recorder Sensor (SRS) / Supply Temperature Sensor (STS)
7.Defrost Temperature Sensor (DTS)
8.Heater Termination Thermostat (HTT)
10.Thermostatic Expansion Valve (TXV)
12.Interrogator Connector (Rear) (ICR)
- - - - -
The reciprocating compressor section includes the compressor (with high pressure switch), power cable storage compartment, and autotransformer.
This section also contains the suction modulating valve, discharge pressure regulating valve, discharge temperature sensor, and discharge/suction pressure transducers.
The return temperature sensor, return recorder sensor, and ambient sensor are located at the right side of the compressor.
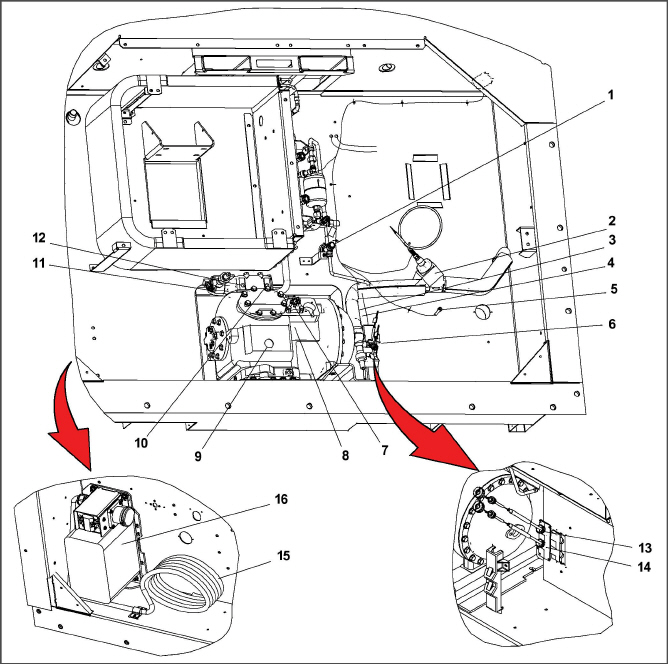
4.Quench Valve Temperature Bulb
9.Compressor Sight Glass View Port
10.Discharge Pressure Transducer
13.Return Temperature Sensor (RTS)
14.Return Recorder Sensor (RRS)
- - - - -
3.1.5Air-Cooled Condenser Section
The air-cooled condenser section (Figure 3.4) consists of the condenser fan, condenser coil, receiver with sight glass/moisture indicator, quench valve, liquid line service valve, filter-drier, condenser pressure transducer, and fusible plug.
The condenser fan pulls air from around the coil and discharges it horizontally through the condenser fan grille.
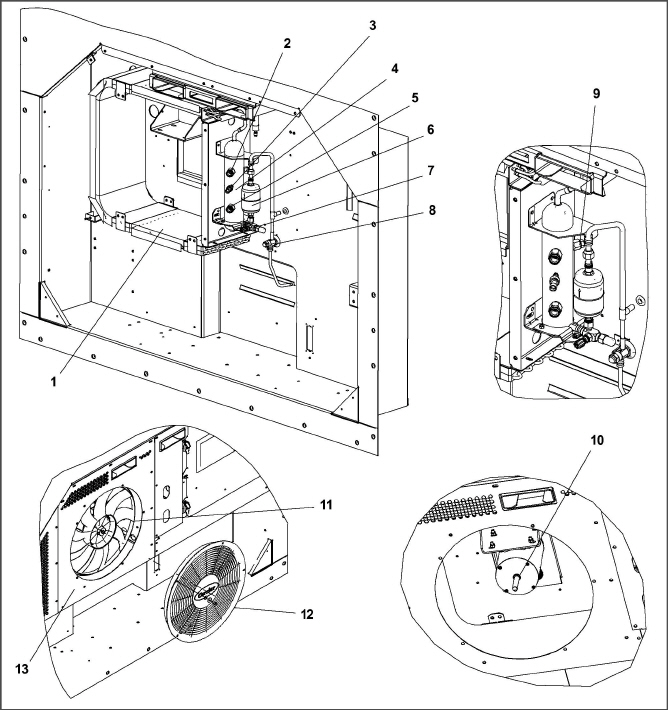
3.Condenser Pressure Transducer
5.Sight Glass/Moisture Indicator
- - - - -
The control box (Figure 3.5) includes the manual operation switches, circuit breaker (CB-1), compressor, fan and heater contactors, control power transformer, current sensor module, controller module and the communications interface module.
3.1.7Communications Interface Module (option)
The communications interface module is a slave module which allows communication between the refrigeration unit and a ship system master central monitoring station. The module will respond to communication, and return information over the ships main power line. Refer to the master system technical manual for further information.
Figure 3.5 Control Box Section
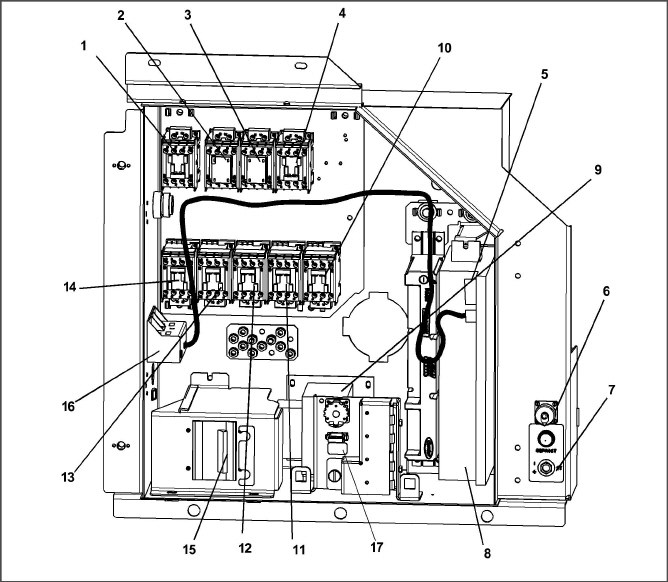
2.Compressor Phase A Contactor − PA
3.Compressor Phase B Contactor − PB
5.Controller/DataCORDER Module (Controller)
6.Remote Monitoring Receptacle
8.Controller Battery Pack (Standard Location)
10.Evaporator Fan Contactor − E1
11.Evaporator Fan Contactor − S1
12.Evaporator Fan Contactor − S2 or EF
13.Evaporator Fan Contactor − E2 or ES
14.Condenser Fan Contactor − CF
15.Circuit Breaker (CB1) − 460V
17.Emergency Bypass Switch (EBS)
- - - - -
Compressor / Motor Assembly |
Number of Cylinders |
6 |
Model |
06DR |
|
CFM |
41 |
|
Weight (Dry) |
118kg (260 lb) |
|
Approved Oil |
Castrol Icematic |
|
Oil Charge degrees |
3.6 liters (7.6 U.S. pints) |
|
Oil Sight Glass |
The oil level range, with the compressor off, should be between the bottom and one-eighth level of the sight glass. |
|
Expansion Valve Superheat |
Verify at -18C (0°F) container box temperature |
4.4 to 6.7°C (8 to 12°F) |
Heater Termination Thermostat |
Opens |
54° (+/− 3) C = 130° (+/− 5) F |
Closes |
38° (+/− 4) C = 100° (+/− 7) F |
|
High Pressure Switch |
Cutout |
25 (+/− 1.0) kg/cm2 = 350 (+/− 10) psig |
Cut-In |
18 (+/− 0.7) kg/cm2 = 250 (+/− 10) psig |
|
EXPLOSION HAZARD:
Failure to follow this WARNING can result in death, serious personal
injury and / or property damage. |
||
Refrigerant |
R−134a |
Conforming to AHRI standard 700 specifications. |
Refrigerant Charge |
Unit Configuration |
Charge Requirements − R-134a |
Receiver |
3.3 kg (7.3 lbs) |
|
When replacing components (g.) and (h.), refer to installation instructions included with replacement part. |
||
Fusible Plug, Receiver* |
Melting point |
99°C = (210°F) |
Torque* |
6.2 to 6.9mkg (45 to 50ft-lbs) |
|
Sight Glass / Moisture Indicator |
Torque |
8.9 to 9.7mkg (65 to 70ft-lbs) |
Condenser Pressure Transducer |
Condenser Fan Starts |
Condenser fan will start if condenser pressure is greater than 14.06kg/cm2 (200psig) OR the condenser fan is OFF for more than 60 seconds. |
Condenser Fan Stops |
Condenser fan will stop if condenser pressure is less than 9.14kg/cm2 (130psig) AND the condenser fan remains ON for at least 30 seconds. |
|
Unit Weight |
Refer to unit model number plate. |
|
* Rupture Disc, part number 14 -00215 -04 may be installed as an alternate for the receiver mounted fusible plug.
Circuit Breaker |
CB-1 |
Trips at 29 amps |
|
CB-2 (50 amps) |
Trips at 62.5amps |
||
CB-2 (70 amp) |
Trips at 87.5amps |
||
Compressor Motor |
Full Load Amps (FLA) |
17.6amps @ 460VAC (with current limiting set at 21 amps) |
|
Condenser Fan Motor |
Nominal Supply |
380 VAC, Three Phase, 50 Hz |
460 VAC, Three Phase, 60 Hz |
Full Load Amps |
.71 amps |
.72 amps |
|
Horsepower |
0.21 hp |
0.36 hp |
|
Rotations Per Minute |
1450 rpm |
1750 rpm |
|
Voltage and Frequency |
360 − 460 VAC +/− 2.5 Hz |
400 − 500 VAC +/− 2.5 Hz |
|
Bearing Lubrication |
Factory lubricated, additional grease not required. |
||
Rotation |
CCW when viewed from shaft end. |
||
Evaporator Coil Heaters |
Number of Heaters |
6 |
|
Rating |
750 watts +5/−10% each @ 230 VAC |
||
Resistance (cold) |
66.8 to 77.2 ohms @ 20°C (68°F) |
||
Type |
Sheath |
||
Evaporator Fan Motor(s) |
|
380 VAC/50 Hz |
460 VAC/60 Hz |
Full Load Amps High Speed |
1.6 |
2.1 |
|
Full Load Amps Low Speed |
0.6 |
0.6 |
|
Nominal Horsepower High Speed |
0.58 |
1.0 |
|
Nominal Horsepower Low Speed |
0.07 |
0.12 |
|
Rotations Per Minute High Speed |
2850 rpm |
3450 rpm |
|
Rotations Per Minute Low Speed |
1425 rpm |
1725 rpm |
|
Voltage and Frequency |
360 − 460 VAC +/− 1.25 Hz |
400 − 500 VAC +/− 1.5 Hz |
|
Voltage & Frequency using power autotransformer |
180 − 230 VAC +/− 1.25Hz |
200 − 250 VAC +/− 1.5 Hz |
|
Bearing Lubrication |
Factory lubricated, additional grease not required |
||
Rotation EF #1 |
CW when viewed from shaft end |
||
Rotation EF #2 |
CCW when viewed from shaft end |
||
Fuses |
Control Circuit |
7.5 amps (F3A, F3B) |
|
Controller / DataCORDER |
5 amps (F1 & F2) |
||
Vent Positioning Sensor |
Electrical Output |
0.5 VDC to 4.5 VDC over 90 degree range |
|
Supply Voltage |
5 VDC +/− 10% |
||
Supply Current |
5 mA (typical) |
||
Humidity Sensor |
Orange wire |
Power |
|
Red wire |
Output |
||
Brown wire |
Ground |
||
Input voltage |
5 vdc |
||
Output voltage |
0 to 3.3 vdc |
||
Output voltage readings verses relative humidity (RH) percentage: |
|||
30% |
0.99V |
||
50% |
1.65V |
||
70% |
2.31V |
||
90% |
2.97V |
||
Controller |
Setpoint Range |
-30 to +30°C ( -22 to +86°F) |
|
3.4Safety and Protective Devices
Unit components are protected from damage by safety and protective devices listed in the following table. These devices monitor the unit operating conditions and open a set of electrical contacts when an unsafe condition occurs.
UNSAFE CONDITION |
SAFETY DEVICE |
DEVICE SETTING |
|---|---|---|
Excessive current draw |
Circuit Breaker (CB-1) − Manual Reset |
Trips at 29 amps (460VAC) |
Circuit Breaker (CB-2, 50 amp) − Manual Reset |
Trips at 62.5 amps (230VAC) |
|
Circuit Breaker (CB-2, 70 amp) − Manual Reset |
Trips at 87.5 amps (230VAC) |
|
Excessive current draw in control circuit |
Fuse (F3A & F3B) |
7.5 amp rating |
Excessive current draw by controller |
Fuse (F1 & F2) |
5 amp rating |
Excessive condenser fan motor winding temperature |
Internal Protector (IP-CM) − Automatic Reset |
N/A |
Excessive compressor motor winding temperature |
Internal Protector (IP-CP) − Automatic Reset |
N/A |
Excessive evaporator fan motor(s) winding temperature |
Internal Protector(s) (IP-EM) − Automatic Reset |
N/A |
Abnormal pressures / temperatures in the high refrigerant side |
Fusible Plug − Receiver |
99°C = (210°F) |
Abnormally high discharge pressure |
High Pressure Switch (HPS) − Automatic Reset |
Open at 25kg/cm@ (350psig) Close at 18kg/cm@ (250psig) |
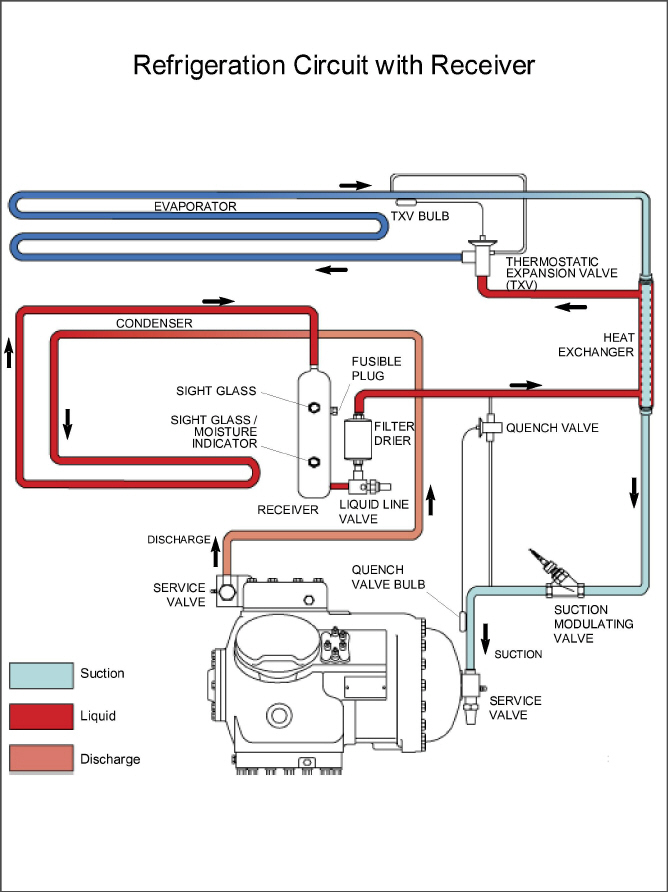
Starting at the compressor (see Figure 3.6), the suction gas is compressed to a higher pressure and temperature.
The gas flows out the compressor through the discharge service valve. Refrigerant gas then moves into the air-cooled condenser, where air flowing across the coil fins and tubes cools the gas to saturation temperature. By removing latent heat, the gas condenses to a high pressure/high temperature liquid and flows to the receiver, which stores the additional charge necessary for low temperature operation.
The liquid refrigerant continues through the liquid line service valve, the filter-drier (which keeps refrigerant clean and dry), and a heat exchanger (that increases subcooling of the liquid) to the thermostatic expansion valve (TXV).
As the liquid refrigerant passes through the variable orifice of the TXV, the pressure drops to suction pressure. In this process some of the liquid vaporizes to a gas (flash gas), removing heat from the remaining liquid. The liquid exits as a low pressure, low temperature, saturated mix. Heat is then absorbed from the return air by the balance of the liquid, causing it to vaporize in the evaporator coil. The vapor then flows through the suction tube back to the compressor.
The TXV is activated by the bulb strapped to the suction line near the evaporator outlet. The valve maintains a constant superheat at the coil outlet regardless of load conditions.
The TXV is a mechanical device that regulates the flow of liquid to the evaporator coil in order to maintain a relatively constant degree of superheat in the gas leaving the evaporator regardless of suction pressure.
The flow of liquid to the evaporator is regulated by a variable orifice which opens to increase refrigerant flow (decrease superheat), or closes to decrease refrigerant flow (increase superheat). The variable orifice is controlled by the temperature sensing bulb which is strapped to the suction line near the evaporator outlet.
During periods of low load, the suction modulating valve (SMV) decreases flow of refrigerant to the compressor. This action balances the compressor capacity with the load and prevents operation with low coil temperatures. In this mode of operation, the quench valve will open as required to provide sufficient liquid refrigerant flow into the suction line for cooling of the compressor motor. The quench valve senses refrigerant condition entering the compressor and modulates the flow to prevent entrance of liquid into the compressor.
The refrigeration system is also fitted with a condenser pressure transducer, which feeds information to the controller. The controller programming will operate the condenser fan so as to attempt to maintain discharge pressures above 130psig in low ambients. At ambients below 27°C (80°F), the condenser fan will cycle on and off depending on condenser pressure and operating times.
1.The condenser fan will start if the condenser pressure is greater than 200psig OR the condenser fan has been OFF for more than 60 seconds.
2.The condenser fan will stop if the condenser pressure is less than 130psig AND the condenser fan has been running for at least 30 seconds.
At ambients above 27°C (80°F), condenser pressure control is disabled and the condenser fan runs continuously.
Figure 3.6 Refrigeration Circuit Schematic